What is the significance of lactobacillus in the formation of curd?
Lactobacillus is a kind of bacteria which can convert a sugar into an alcohol and then into an acid by means of anaerobic respiration.
Milk contains a sugar called lactose, a disaccharide (compound sugar) made by the glycosidic bonding between glucose and glactose (monosaccharides).
When milk is heated to a temperature of 30-40 degrees centigrade and a small amount of old curd added to it, the lactobacillus in that curd sample gets activated and multiplies. These convert the lactose into lactic acid, which imparts the sour taste to curd.
skip to main |
skip to sidebar
![]()

SAVE WATER.



Gone are the dull book days !!!!!!

symmetry in a tiger

smart classroom

Kulachi Hansraj Model School


Use dustbins!

The key to the protection and care of the Earth




Opaque objects cast distinct shadows


Karanjot V B

Shadows and eclipses



Love and care your environment!

A PLEDGE BY YOUNG KULACHIANS TO SAVE THE EARTH!


Monocot and Dicot seed

The only living things to capture Sun's energy
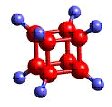
atoms

WELCOME TO MY FUN SCIENCE BLOG
I am Savita Dhutti,a science teacher at a well established public school in India.I welcome all of you to My science mania ! Its a website,I created for sharing e-learning experience with my students.Science is in fact, a real fun.It is a subject never--never confined within the four walls of the clssroom.Science is a continuous process of learning! I wish to create a pleasing learning environment for my students.So, Come and ENJOY Science with me.
class 8 BIOLOGY H HW
Biology
Make a project on the following topic
Microorganisms
The following aspects should be properly covered.
- Different group of microorganisms 5 characteristics of each
Algae, Fungi, Bacteria, Protozoa, Virus Microorganisms as friends in Food, Medicine, Agriculture, Nature, Industry and Microorganisms as Foes.
Use A4 size sheets and put them inside an Eco friendly Folder.
Be thorough with whatever you write, you will be orally assessed.
Labels
- A CALL for the students....... (6)
- A student showing solar eclipse (1)
- An Intelligent mind rests in a healthy body. (1)
- BIOLOGY (1)
- Body systems diagrams for practice (2)
- Chant Gayatri Mantra daily and live life fully. (1)
- class 8 HHW BIOLOGY (10)
- CLASS VII HOLIDAYS HOME WORK (8)
- click to enlarge and print (1)
- cow dung.holidays home work reference (18)
- electric current (13)
- fabric from fiber (4)
- food class 6th (24)
- global concern (8)
- global warming (6)
- Information (1)
- Information: symmetry (2)
- Jupiter facts (1)
- life cycles of animals (1)
- light and shadows (4)
- link to my slideshow (1)
- magnets (2)
- nature of matter (2)
- plant structure and function (7)
- plants (9)
- plants image gallary (2)
- properties of matter (3)
- puzzle clues (1)
- Seed germination (1)
- SHIVLING AT the AMARNATH TEMPLE HAS MELTED. (1)
- Student Activity (43)
- student Corner (47)
- student information (10)
- Syllabus Class V / SCIENCE / FIRST TERM (1)
- Take A break (1)
- water facts (6)
- word bank plants (2)
- work and energy (11)
- धरती को बचाने की कोशिश (1)
- प्लांट growth (1)
Total Pageviews
shadow dancing
Facebook Badge
e teachers of india my badge
welcome to my science mania!!!!!!!
I am Savita Dhutti,a science teacher at a well established public school in India.I welcome all of you to My science mania ! Its a website,I created for sharing e-learning experience with my students.Science is in fact, a real fun.It is a subject never--never confined within the four walls of the clssroom.Science is a continuous process of learning! I wish to create a pleasing learning environment for my students.
So, Come and ENJOY Science with me.
So, Come and ENJOY Science with me.
global warming
NeoCounter
NeoPod
NeoFlags
EVERY DROP OF WATER IS PRECIOUS.

SAVE WATER.
water
VI H celebrating Talent Show 2007

Labels
- A CALL for the students....... (6)
- A student showing solar eclipse (1)
- An Intelligent mind rests in a healthy body. (1)
- BIOLOGY (1)
- Body systems diagrams for practice (2)
- Chant Gayatri Mantra daily and live life fully. (1)
- class 8 HHW BIOLOGY (10)
- CLASS VII HOLIDAYS HOME WORK (8)
- click to enlarge and print (1)
- cow dung.holidays home work reference (18)
- electric current (13)
- fabric from fiber (4)
- food class 6th (24)
- global concern (8)
- global warming (6)
- Information (1)
- Information: symmetry (2)
- Jupiter facts (1)
- life cycles of animals (1)
- light and shadows (4)
- link to my slideshow (1)
- magnets (2)
- nature of matter (2)
- plant structure and function (7)
- plants (9)
- plants image gallary (2)
- properties of matter (3)
- puzzle clues (1)
- Seed germination (1)
- SHIVLING AT the AMARNATH TEMPLE HAS MELTED. (1)
- Student Activity (43)
- student Corner (47)
- student information (10)
- Syllabus Class V / SCIENCE / FIRST TERM (1)
- Take A break (1)
- water facts (6)
- word bank plants (2)
- work and energy (11)
- धरती को बचाने की कोशिश (1)
- प्लांट growth (1)

Its e-teaching time now!!!!!!!!!!!

Gone are the dull book days !!!!!!
CII Shiksha India's website
CII SHIKSHA INDIA IS A NON PROFIT ORGANIZATION ........
CII SHIKSHA INDIA IS A NON PROFIT ORGANIZATION ........WHICH STARTED ITS .........
e-teaching learning portal in January 2007 inagurated by President Abdul Kalam Azad and is continuously guiding teachers to work in collaboration on Shiksha portal for taking India to the new horizons of E-teaching learning.I have been assosiated with it and working on e-teaching learning.The portal had announced a contest for its teachers for contribution to the portal and myself ,the recipient of the award is happy to be assosiated to the portal and in being able to explore net and other e-tools for teaching.
e-teaching learning portal in January 2007 inagurated by President Abdul Kalam Azad and is continuously guiding teachers to work in collaboration on Shiksha portal for taking India to the new horizons of E-teaching learning.I have been assosiated with it and working on e-teaching learning.The portal had announced a contest for its teachers for contribution to the portal and myself ,the recipient of the award is happy to be assosiated to the portal and in being able to explore net and other e-tools for teaching.
symmetry

symmetry in a tiger
e-learning is fun!

smart classroom
alphabets in nature
This album is powered by BubbleShare - Add to my blog
MY SCHOOL

Kulachi Hansraj Model School
KULACHI BLOGGERS CLUB

Manage the waste

Use dustbins!
Student Awareness

The key to the protection and care of the Earth
Protecting Earth together

Student corner
- 1. Poem by Megha Panjwani VI H
- 2. Vasu Mittal says........
- 3. Poem by Manmeet Kaur VI H

Do you think talent shows in the school are worth it or a wastage of time?
Items for the talent show of my class
- On the spot Poetry competition
- science facts
- Making invitation cards for the guests
- Rangoli making
- wecome song by girls
- art and craft display
- Singing bhajan
- folk dance boys(solo)
- folk dance girls(solo)
- group dance by boys
- group dance by girls
- drama
- playing music instument
- short humourous skit
solar eclipse

shadow formation activity PARAS V B

Opaque objects cast distinct shadows
global warming

Shadow is not formed by transparent objects

Karanjot V B
class V activity

Shadows and eclipses

url=http://savitadhuttimyscienceatkulachi.blogspot.com" id="clustrMapsLink">
click for the details
time is ticking away fast
Labels
- A CALL for the students....... (6)
- A student showing solar eclipse (1)
- An Intelligent mind rests in a healthy body. (1)
- BIOLOGY (1)
- Body systems diagrams for practice (2)
- Chant Gayatri Mantra daily and live life fully. (1)
- class 8 HHW BIOLOGY (10)
- CLASS VII HOLIDAYS HOME WORK (8)
- click to enlarge and print (1)
- cow dung.holidays home work reference (18)
- electric current (13)
- fabric from fiber (4)
- food class 6th (24)
- global concern (8)
- global warming (6)
- Information (1)
- Information: symmetry (2)
- Jupiter facts (1)
- life cycles of animals (1)
- light and shadows (4)
- link to my slideshow (1)
- magnets (2)
- nature of matter (2)
- plant structure and function (7)
- plants (9)
- plants image gallary (2)
- properties of matter (3)
- puzzle clues (1)
- Seed germination (1)
- SHIVLING AT the AMARNATH TEMPLE HAS MELTED. (1)
- Student Activity (43)
- student Corner (47)
- student information (10)
- Syllabus Class V / SCIENCE / FIRST TERM (1)
- Take A break (1)
- water facts (6)
- word bank plants (2)
- work and energy (11)
- धरती को बचाने की कोशिश (1)
- प्लांट growth (1)
my school's location through google earth

calender
clicks on my blog
Science is not just a subject of teaching learning.It is a way of knowing about,thinking about and caring about the environment of which we are a part.
Labels
- A CALL for the students....... (6)
- A student showing solar eclipse (1)
- An Intelligent mind rests in a healthy body. (1)
- BIOLOGY (1)
- Body systems diagrams for practice (2)
- Chant Gayatri Mantra daily and live life fully. (1)
- class 8 HHW BIOLOGY (10)
- CLASS VII HOLIDAYS HOME WORK (8)
- click to enlarge and print (1)
- cow dung.holidays home work reference (18)
- electric current (13)
- fabric from fiber (4)
- food class 6th (24)
- global concern (8)
- global warming (6)
- Information (1)
- Information: symmetry (2)
- Jupiter facts (1)
- life cycles of animals (1)
- light and shadows (4)
- link to my slideshow (1)
- magnets (2)
- nature of matter (2)
- plant structure and function (7)
- plants (9)
- plants image gallary (2)
- properties of matter (3)
- puzzle clues (1)
- Seed germination (1)
- SHIVLING AT the AMARNATH TEMPLE HAS MELTED. (1)
- Student Activity (43)
- student Corner (47)
- student information (10)
- Syllabus Class V / SCIENCE / FIRST TERM (1)
- Take A break (1)
- water facts (6)
- word bank plants (2)
- work and energy (11)
- धरती को बचाने की कोशिश (1)
- प्लांट growth (1)
Class VI Students ! Refer this site for help in your Science Project given as Holidays H.W.
Saving Earth's Resources
seed germination
Planting a green friend -- a sapling !

Love and care your environment!
a pledge by the Students in the VANAMAHOTSAVA function

A PLEDGE BY YOUNG KULACHIANS TO SAVE THE EARTH!
plant growth

Seed Germination

Monocot and Dicot seed
A Typical Flowering Plant

The only living things to capture Sun's energy
Labels
- A CALL for the students....... (6)
- A student showing solar eclipse (1)
- An Intelligent mind rests in a healthy body. (1)
- BIOLOGY (1)
- Body systems diagrams for practice (2)
- Chant Gayatri Mantra daily and live life fully. (1)
- class 8 HHW BIOLOGY (10)
- CLASS VII HOLIDAYS HOME WORK (8)
- click to enlarge and print (1)
- cow dung.holidays home work reference (18)
- electric current (13)
- fabric from fiber (4)
- food class 6th (24)
- global concern (8)
- global warming (6)
- Information (1)
- Information: symmetry (2)
- Jupiter facts (1)
- life cycles of animals (1)
- light and shadows (4)
- link to my slideshow (1)
- magnets (2)
- nature of matter (2)
- plant structure and function (7)
- plants (9)
- plants image gallary (2)
- properties of matter (3)
- puzzle clues (1)
- Seed germination (1)
- SHIVLING AT the AMARNATH TEMPLE HAS MELTED. (1)
- Student Activity (43)
- student Corner (47)
- student information (10)
- Syllabus Class V / SCIENCE / FIRST TERM (1)
- Take A break (1)
- water facts (6)
- word bank plants (2)
- work and energy (11)
- धरती को बचाने की कोशिश (1)
- प्लांट growth (1)
molecules in nature

"Welcome to the planet science"
Welcome to the exciting world of Science!
This is my planet science-----A fun filled planet full of multiple activities,interesting videos, thought provoking articles on contemporary science issues,puzzles , compiled images and much more.....
Atoms---- the constituent particles of matter

atoms
Blog Archive
-
►
2007
(134)
- ► 05/06 - 05/13 (13)
- ► 05/13 - 05/20 (19)
- ► 05/20 - 05/27 (13)
- ► 05/27 - 06/03 (11)
- ► 06/10 - 06/17 (1)
- ► 07/01 - 07/08 (4)
- ► 07/08 - 07/15 (11)
- ► 07/15 - 07/22 (11)
- ► 07/29 - 08/05 (11)
- ► 08/05 - 08/12 (3)
- ► 08/12 - 08/19 (12)
- ► 08/19 - 08/26 (3)
- ► 09/09 - 09/16 (10)
- ► 09/16 - 09/23 (3)
- ► 09/30 - 10/07 (3)
- ► 10/07 - 10/14 (2)
- ► 12/09 - 12/16 (4)
-
►
2008
(137)
- ► 01/06 - 01/13 (2)
- ► 01/13 - 01/20 (3)
- ► 01/20 - 01/27 (6)
- ► 01/27 - 02/03 (11)
- ► 02/10 - 02/17 (2)
- ► 02/17 - 02/24 (2)
- ► 03/16 - 03/23 (2)
- ► 03/23 - 03/30 (3)
- ► 03/30 - 04/06 (1)
- ► 04/06 - 04/13 (33)
- ► 05/04 - 05/11 (4)
- ► 05/11 - 05/18 (1)
- ► 05/18 - 05/25 (3)
- ► 06/08 - 06/15 (6)
- ► 06/29 - 07/06 (1)
- ► 07/13 - 07/20 (1)
- ► 08/10 - 08/17 (7)
- ► 08/17 - 08/24 (5)
- ► 08/31 - 09/07 (1)
- ► 09/14 - 09/21 (1)
- ► 09/21 - 09/28 (2)
- ► 09/28 - 10/05 (6)
- ► 11/23 - 11/30 (17)
- ► 11/30 - 12/07 (4)
- ► 12/14 - 12/21 (10)
- ► 12/21 - 12/28 (3)
-
►
2009
(44)
- ► 01/18 - 01/25 (2)
- ► 02/08 - 02/15 (5)
- ► 03/22 - 03/29 (2)
- ► 03/29 - 04/05 (1)
- ► 04/12 - 04/19 (1)
- ► 05/03 - 05/10 (8)
- ► 05/10 - 05/17 (1)
- ► 05/24 - 05/31 (17)
- ► 07/26 - 08/02 (1)
- ► 10/25 - 11/01 (3)
- ► 12/20 - 12/27 (3)
-
►
2010
(16)
- ► 01/17 - 01/24 (1)
- ► 01/24 - 01/31 (4)
- ► 01/31 - 02/07 (3)
- ► 05/30 - 06/06 (6)
- ► 08/29 - 09/05 (1)
- ► 10/03 - 10/10 (1)
Hi ! I AM A SCIENCE TEACHER.

- savitadhutti
- Delhi, Delhi, India
- I AM A SCIENCE TEACHER IN A WELL REPUTED SCHOOL IN INDIA. I AM A MEMBER OF e-shiksha CLUB. I HAVE JOINED TEACHERTUBE FORUM AS WELL. I AM EXPLORING NET TO LEARN AND SHARE.
Nature and you
MOLECULES IN NATURE FORM BONDS JUST LIKE YOU ARE BONDED TO YOUR FRIENDS.


